Toyota Ups Its Corporate Solar Capacity
Toyota will add 30 megawatts of solar capacity at its engine plant in Huntsville, Alabama—part of several renewable energy upgrades across its North American manufacturing facilities.
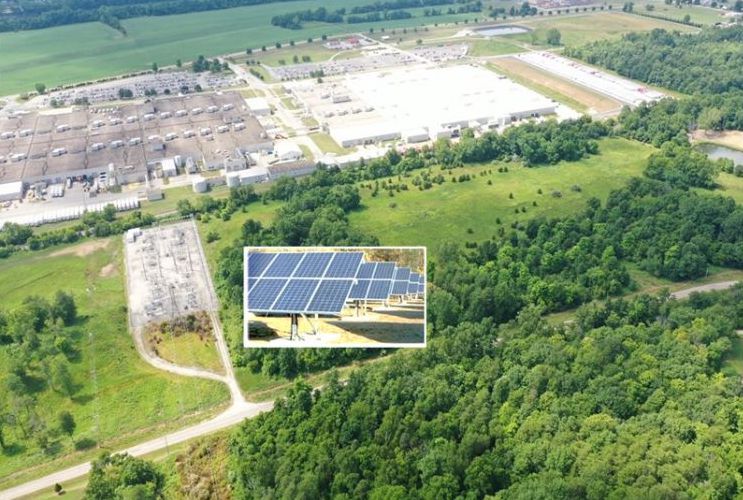
Japan-headquartered car giant Toyota recently announced plans to add a 30-megawatt (MW) solar project at its Huntsville engine manufacturing facility in northern Alabama.
A rendering of Toyota’s upcoming 168-acre solar project, situated outside its engine plant in Alabama’s North Huntsville Industrial Park. Image used courtesy of Toyota
The $49 million project is touted as the largest flexibility site in the region, spanning 168 acres and generating 62 gigawatt-hours (GWh) of renewable electricity annually—enough to serve more than 5,600 homes. The new array means more than 70% of the plant will be solar-powered, saving around 22,000 metric tons of yearly carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions.
Toyota signed a power purchase deal involving municipal utility firm Huntsville Utilities and two subsidiaries: Toyota Alabama and Toyota Tsusho America. The latter will manage the construction (scheduled to start this spring) and run the site’s long-term operations after it comes online next summer.
The project brings Toyota’s total investment in the plant to $1.5 billion through six expansions since production launched in 2003. With nearly 2,000 employees, the site assembled over 665,000 hybrid and conventional engines in 2022 for the company’s Tundra, Corolla Cross, and Sienna lineups.
Solar Installations at Toyota Plants
The move supports Toyota’s broader CO2 emissions-reduction targets. The company aims to reach “carbon-neutral” status across all of its manufacturing facilities by 2035, then scaling up to eliminate CO2 emissions by 2050.
Building on- and off-site solar and wind projects is one of its mechanisms to achieve this goal. Toyota announced in 2022 that its logistics port facility in Long Beach—the largest of its North American port facilities, processing around 200,000 vehicles annually—is nearing carbon neutrality after renovations added hydrogen fuelling stations for its heavy-duty vehicles and a plant producing hydrogen fuel from agricultural waste-sourced biogas.
Its latest solar project in Alabama marks a step up from Toyota’s previous renewable renovations. Its Huntsville engine plant received $2.7 million in 2021 to build a 3.3-acre solar array, adding 1.6 MW in capacity. That project was one of three new solar arrays spanning 10.8 acres in Alabama, Missouri, and West Virginia, offsetting 6.48 GWh of energy annually. The trio represented an investment of $9.3 million and added nearly 5 MW of solar capacity.
In 2021, Toyota added a solar array to its engine and transmission plant in Buffalo, West Virginia. Image used courtesy of Toyota
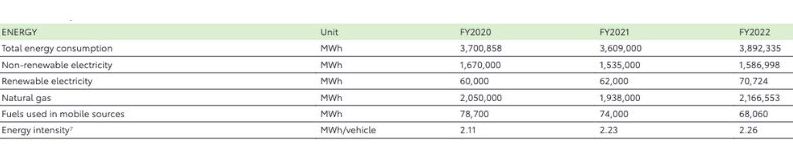
According to Toyota’s latest North American Environmental Sustainability Report, its greenhouse grass (GHG) efficiency improvements and on-site solar projects avoided 21,975 metric tons of CO2 in 2022 alone. Most of that figure (nearly 19,000 metric tons) was tied to “Scope 2” emissions, which includes consumption of purchased electricity across its North American sites. The report also mentioned that 22% of Toyota Motor North America’s electricity consumption is expected to come from renewables beginning in 2023.
By 2030, Toyota plans to cut its GHG emissions in half from 2018 levels across nine U.S.-based plants through energy efficiency upgrades and renewable expansions. It will also boost its purchased renewables by at least 45% of its total electricity purchased in North America. While that figure stood at only 4.1% in late 2022, the company expects its share to grow as its first virtual power purchase agreements come online.
This chart from Toyota’s 2022 North American Environmental Sustainability Report (page 34) shows the company’s progress in sourcing renewable electricity and phasing out its use of natural gas and non-renewables. Image used courtesy of Toyota
Outside of its operations, Toyota targets a 90% reduction in CO2 emissions (compared to 2010 levels) from its new vehicle models by 2050. Its electric vehicle expansion plan earmarks around $35 billion to reach 3.5 million EV sales per year across 30 models by the end of the decade.
Earlier this month, the company set a new goal to grow its battery-electric vehicle (BEV) lineup by ten new models before 2026, expecting to yield 1.5 million sales.
Corporate Solar Adoption Soars
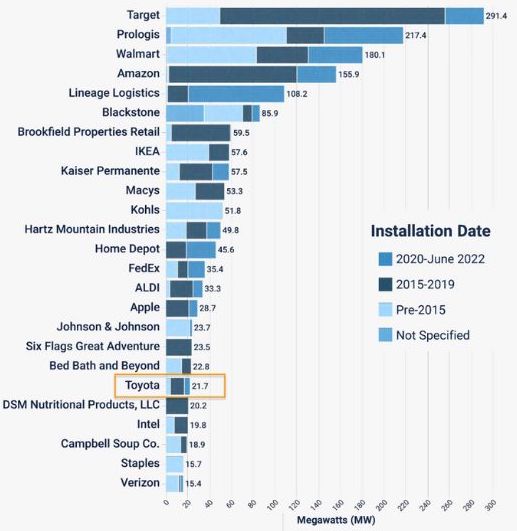
Toyota is among the top corporations installing on-site solar panels in the U.S., according to data from the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA). The leading adopters of corporate solar use account for around 19 GW of capacity across nearly 50,000 facilities nationwide as of June 2022.
Corporate solar systems represent around half of all commercial solar capacity installed since 2020, suggesting a burgeoning market as companies increase their off-site solar procurement. More than two-thirds of all off-site corporate solar came online in the years since 2020.
SEIA tracks this emerging market through its Solar Means Business report, the latest of which tallies some 48,000 projects collectively generating enough annual power for more than 3 million homes. Though Toyota is ranked 52nd overall for its corporate solar use, it dominates the automotive category, claiming 21.7 MW of on-site capacity, behind Volkswagen (10.8 MW) and General Motors (6.1 MW).
Top 25 corporate users by installed on-site solar capacity. Image used courtesy of SEIA (emphasis on Toyota added by EE Power)
Breaking the data apart by location, Toyota is among the top corporate solar users in Kentucky, Mississippi, West Virginia, Alabama, and Missouri, alongside other industry titans like Walmart and Meta.