NGK Insulators, Ltd. announced that its Zinc rechargeable battery, which is currently under development, acquired the world's first UL verification mark in the battery energy storage systems field as a result of testing based on c the UL 9540A standard by UL. UL9540A is a Test Method for Evaluating Thermal Runaway Fire Propagation in Battery Energy Storage Systems. Zinc rechargeable battery's high safety performance has been demonstrated through the objective and highly reproducible verification process undertaken by UL.
NGK is currently developing Zinc rechargeable battery as a battery energy storage system (rechargeable battery) that realizes high safety and large energy storage capacity, making it optimal for indoor installation. This has been achieved by using zinc as the negative electrode, aqueous solution as the electrolytic solution, and NGK's unique ceramic separator as a barrier between the positive and negative electrodes.
Batteries that employs zinc as the negative electrode have a high energy density. This has allowed zinc batteries to be widely used as single-use, non-rechargeable batteries, such as alkaline batteries and air cells for hearing aids, etc. However, when zinc is used as the negative electrode of a rechargeable battery, the zinc will form dendrites on the negative electrode during charging. The dendrites will then pierce the separator and will cause a short circuit. For many years, this problem has hindered the progress on the commercialization of zinc rechargeable batteries.
You may also like: 1000 Kilometers of Range for EVs with Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
NGK has solved this problem by developing a new highly densified ceramic separator with hydroxide (OH-) ion conductivity.As a result, NGK has succeeded in developing a zinc rechargeable battery. The new ceramic separator developed by NGK allows only the hydroxide (OH-) ions, which are essential for battery operation, to pass, while physically blocking the dendrites, thereby preventing short circuits between the positive and negative electrodes.
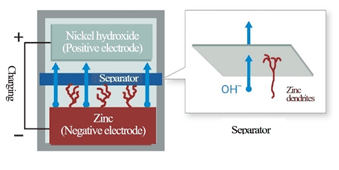 Ceramic separator with a highly densified structure allows hydroxide (OH-) ions to pass while physically blocking the penetration of zinc.
Ceramic separator with a highly densified structure allows hydroxide (OH-) ions to pass while physically blocking the penetration of zinc.
The separator has thus made it possible for the battery to undergo repeated charging and discharging cycles. This is the first case that a ceramic separator is used for a zinc rechargeable battery.
Zinc rechargeable battery offers a high energy density and compact installation, and the battery can be operated at room temperature. In addition, Zinc rechargeable battery does not have the risk of internal fire or thermal runaway as it employs a nonflammable aqueous solution as an electrolytic solution. Therefore, Zinc rechargeable battery features high safety, and it is also optimal for indoor installation.
Recommended for you: ProLogium’s Solid-State Batteries Powering Explosion-Proof Products
There is a strong need for battery energy storage systems that offers both high safety and large energy storage capacity at schools and hospitals, retail facilities such as convenience stores, and facilities where business continuity planning (BCP) measures are crucial, such as base stations and communications buildings. NGK envisions that Zinc rechargeable battery will be adopted for use in such facilities.
The UL 9540A standard establishes test methods to confirm what could happen if there were a thermal runaway within a battery energy storage system. The standard was developed by UL at the request of fire departments and fire protection organizations in the United States. It has now gained a high level of trust around the world, not only in the United States, where strict safety standards are required.
The UL 9540A tests are conducted to confirm the risks associated with fire, flaming, fragment dispersion, fuming, and flammable gas generation. It has been confirmed that NGK's Zinc rechargeable battery will not cause thermal runaway or fire, as a result of surface heating, overcharging, over-discharging and nail penetration tests carried out at the cell level in accordance with UL 9540A test methods. Based on these results, NGK will promote Zinc rechargeable battery as a product that is optimal for installation in places where a high degree of safety is required, such as indoors.
There has been heightened interest in the effective use of renewable energy, peak shaving for electric power, securing electric power during disasters, and BCP measures. Against this backdrop, the demand for battery energy storage systems has been expected to grow in recent years. Since 2015, NGK has been working to develop Zinc rechargeable battery into a product featuring advanced fire safety performance, large energy storage capacity, and long life.
NGK has been pushing ahead with efforts to commercialize Zinc rechargeable battery at the earliest opportunity. Notably, in 2016, the Ceramics Battery Project was formed as a company-wide project with participation from various parts of the company, including the corporate R&D and the Corporate Manufacturing Engineering and Sales and Marketing Divisions, along with the Intellectual Property and Purchasing Departments.
With the acquisition of the UL verification mark, NGK will further accelerate development and demonstration tests, with plans to commercialize Zinc rechargeable battery in fiscal year 2020.






