AI-Enabled 3D Models Tackle Critical Challenges for Utilities
AI tools simulate the effects of extreme weather events, pinpoint vegetation risks, and reduce time-consuming manual surveys across utility networks.
Artificial intelligence-enabled tools from Australian startup Neara allow utilities to create detailed maps of their networks and simulate the impact of wildfires, flooding, hurricanes, and other extreme weather events on their assets. These 3D models can identify the most vulnerable equipment and visualize the effect of potential upgrades, such as a covered conductor or a higher clearance.
Neara starts by building a physics-informed digital twin of a utility’s network. Overlays offer multiple layers incorporating GIS data, LiDAR scans, operating conditions, inspection records, satellite imagery, and weather data like temperature and wind speed. The digital twin includes CAD designs and engineering specifications with dimensions and components for poles, conductors, and cross-arm.
Neara simulates wildfire impacts across utility networks. Image used courtesy of Neara
Neara’s LiDAR technology assigns classes to trees, buildings, poles, vegetation, antennas, and other roof objects with 99% precision. The company claims its automated LiDAR system can classify more than 1,000 miles daily.
Neara’s LiDAR classification. Image used courtesy of Neara
AI modeling helps utilities prepare for extreme weather events with predictive data on precipitation, wind speed and direction, storm surge, and ice and snow exposure. For example, a distribution line in an area with increased rain may need to raise the clearance by several feet to prevent outages.
Neara can simulate failure conditions and spot high-risk assets before an event occurs. If the platform finds vegetation overgrowth in a high-voltage danger zone, crews could be sent out for pruning and clearance. It also calculates the distance of trees near lines and simulates strike potential.
Wildfire Prevention and Weather Resilience
Manual vegetation management strategies fall short of addressing today’s increasingly expansive wildfires, often fed by extended heat waves and droughts. Per the Environmental Protection Agency, the typical acreage burned annually has widened since the 1980s.
Utility infrastructure has historically accounted for under 10% of wildfires. But when power lines do ignite, the damage tends to be significant. About half of California’s most destructive fires were linked to power lines, according to the California Public Utilities Commission.
Utilities keep track of power assets through periodic field visits, which are subject to human error and may be limited in visualizing territory. Neara’s platform automates this task with 3D models identifying vegetation encroachment and simulations mapping wildfire impacts. The company recently landed a multi-year contract to deploy this capability across Southern California Edison’s 50,000-square-mile service territory.
Neara’s flood management models. Image used courtesy of Neara
Several other utilities are using Neara’s tools. As of September 2023, the platform managed 1 million square miles and 8 million assets where vegetation could impact electrical equipment. It came in handy when Australia-based SA Power Networks needed to assess network damage and risk from the historic River Murray Flood in 2022 and 2023. Neara’s AI models needed only 15 minutes to analyze the flood area’s 21,000 powerline spans, a process that otherwise would entail months of manual work. The utility gauged impacts on its distribution assets at different water levels and predicted the time and location of power lines breaching clearances or requiring disconnection.
In another case study, record floods caused significant outages across a network owned by Australian utility Endeavour Energy. Within two days of using Neara for emergency flood mitigation, the company activated a real-time model based on live flood sensors and open-source data to measure rising waters. Overall, Neara helped Endeavour eliminate 300 hours of manual inspections.
AI Tools in the Power Industry
Neara is following a heightened demand for AI tools in the power industry, with some top utilities already infusing generative AI into their operations. In Deloitte’s 2023 Power and Utilities Industry Survey, executives cited operational efficiency and performance improvements as the top benefit of integrating AI into electric power systems, followed by increased accuracy in demand forecasting and resource allocation. Other benefits include streamlining maintenance and expanding renewable utilization.
Using finite element analysis techniques, Neara calculates stress on asset components (left) and maps areas at risk for cascading pole failure (right). Image used courtesy of Neara
Neara’s platform serves a range of demands for utilities, including network-wide structural analysis. It measures stress, tension, and precise loading on assets, using static and finite element analysis (FEA) to assess the integrity of poles, cross-arms, insulators, and other components. For example, its FEA-optimized tools detect cascading pole failure, where the tension from a single pole falling causes ripple effects on adjacent components.
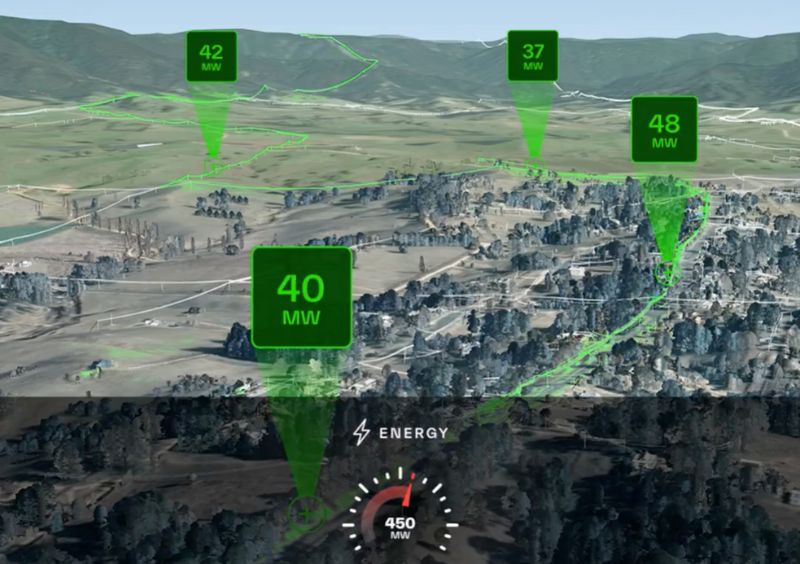
AI modeling can also identify latent capacity in existing networks. Neara’s heat maps visualize locations where renewables could be connected. The digital twin plots ideal transmission routes based on terrain constraints, clearance requirements, easements, and derating considerations.
This heat map highlights locations where an existing network can be expanded to connect new renewable energy resources. Image used courtesy of Neara
Neara also assists with dynamic line rating (DLR), where electrical conductors are rated based on real-time weather conditions and power flow. Unlike conventional static line ratings, which rely on conservative estimates of the transmission line’s operating environment, DLR analysis reveals additional unused capacity by understanding the transmission line’s dynamic constraints in real-world scenarios.
With Neara, system operators can dynamically rate transmission lines with targeted data on ambient temperature, solar irradiation, and wind speeds.